Video System - Cameras
While much can be said about camera selection and/or camera technology in general we prefer to begin the dialogue with a simple, yet profound graphic on the subject...
Cameras are found in a wide variety of shapes and sizes...
...however there are only three (3) basic types of camera technology...
... Analog,
... HD Hi Definition, Serial Digital Interface, and,
... IP Internet Protocol
There are many features that define even the simplest video cameras but the single most important aspect that affects picture quality is resolution.
CCTV RESOLUTION EXPLAINED
Summarizing the remainder of this page... Video image quality is a function of the number of horizontal pixels multiplied by the number of vertical pixels that make up a given image. The best analog images are 720 pixels wide x 480 pixels tall. This translates to 350,000 pixels per image or about 1/3 Mega-Pixel. HD-SDI camera images are either 1280 x 720 (720p) or 1920 x 1080 (1080p) pixels which translates to about 1 and 2.1Mp respectfully. Finally, IP cameras are capable of delivering even greater resolutions - 1.3, 2.0, 3.0, 5 and 10Mp are all (for example) common IP camera resolutions.
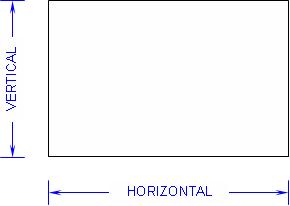
Now, for those who may appreciate a more complete development of a technical concept... video cameras, regardless if we’re referring to those used in security systems or the really expensive variety that provide our favorite sport’s instant replays, all provide an image that is made up of small digital components called pixels. The format of every video image is defined by the number of Horizontal pixels and the number of Vertical pixels. Perhaps the simple diagram below will provide an better understanding?
... Analog,
... HD Hi Definition, Serial Digital Interface, and,
... IP Internet Protocol
There are many features that define even the simplest video cameras but the single most important aspect that affects picture quality is resolution.
CCTV RESOLUTION EXPLAINED
Summarizing the remainder of this page... Video image quality is a function of the number of horizontal pixels multiplied by the number of vertical pixels that make up a given image. The best analog images are 720 pixels wide x 480 pixels tall. This translates to 350,000 pixels per image or about 1/3 Mega-Pixel. HD-SDI camera images are either 1280 x 720 (720p) or 1920 x 1080 (1080p) pixels which translates to about 1 and 2.1Mp respectfully. Finally, IP cameras are capable of delivering even greater resolutions - 1.3, 2.0, 3.0, 5 and 10Mp are all (for example) common IP camera resolutions.
Now, for those who may appreciate a more complete development of a technical concept... video cameras, regardless if we’re referring to those used in security systems or the really expensive variety that provide our favorite sport’s instant replays, all provide an image that is made up of small digital components called pixels. The format of every video image is defined by the number of Horizontal pixels and the number of Vertical pixels. Perhaps the simple diagram below will provide an better understanding?
Multiplying the Number of Horizontal pixels by the Number of Vertical pixels in a picture provides the total number of pixels that define the image’s resolution. Digital Video Recorders (DVR’s) record typical analog cameras at a resolution that is called CIF (Common Intermediate Format) and is defined as 352 (pixels horizontal) x 240 (pixels vertical). Newer, more expensive recorders can offer analog camera recording capacity of 4CIF (2 x Horizontal – 704 pixels by 2 x Vertical – 480 pixels) and even more recent changes provide a slightly better resolution (720 x 480) which the industry calls “D1.”
If we do the math (multiply the horizontal resolution by the vertical resolution) we come up with total pixels per picture these analog technologies deliver.
CIF = 352 x 240 = 84,480 pixels
D1 = 720 x 480 = 345,600 pixels
HD Cameras (HD-SDI) as a brief comparison, provide…
HD (720p) = 1280 x 720 = 921,600 pixels
HD (1080p) = 1920 x 1080 = 2,073,600 pixels
Note this big number has led to the creation of another “industry speak” definition – MegaPixel – which stands for million pixels. The typical HD camera with 2,073,600 is often referred to as having 2.1 MegaPixel (MP) resolution.
Internet Protocol (IP) cameras (yet another camera technology) can provide even higher resolutions of…
3 MP = 2048 x 1536 = 3,145,728 pixels
5 MP = 2592 x 1944 = 5,038,848 pixels
10 MP = 3648 x 2752 = 10,039,296 pixels
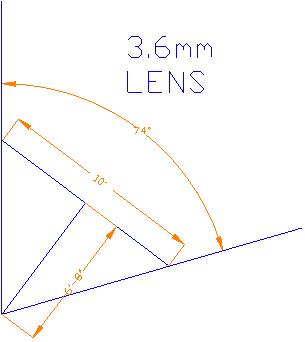
The drawing (below) – a typical 3.6mm (focal length) camera example – is one we’ll use to detail how image resolution influences video quality.
If we do the math (multiply the horizontal resolution by the vertical resolution) we come up with total pixels per picture these analog technologies deliver.
CIF = 352 x 240 = 84,480 pixels
D1 = 720 x 480 = 345,600 pixels
HD Cameras (HD-SDI) as a brief comparison, provide…
HD (720p) = 1280 x 720 = 921,600 pixels
HD (1080p) = 1920 x 1080 = 2,073,600 pixels
Note this big number has led to the creation of another “industry speak” definition – MegaPixel – which stands for million pixels. The typical HD camera with 2,073,600 is often referred to as having 2.1 MegaPixel (MP) resolution.
Internet Protocol (IP) cameras (yet another camera technology) can provide even higher resolutions of…
3 MP = 2048 x 1536 = 3,145,728 pixels
5 MP = 2592 x 1944 = 5,038,848 pixels
10 MP = 3648 x 2752 = 10,039,296 pixels
The drawing (below) – a typical 3.6mm (focal length) camera example – is one we’ll use to detail how image resolution influences video quality.
A typical 3.6 mm lens provides a horizontal field of view of 74°. At a distance of 6’-8” this lens will provide a 10’ wide (horizontal) field of view. The image of a person (~2 feet wide) standing at this distance would be created from about …
75 (horizontal) pixels when recorded at CIF,
150 (horizontal) pixels (~2x CIF) when recorded at D1, and,
385 (horizontal) pixels (~5x CIF) when recorded at HD.
When considering the post recorded zoom capability of the HD image, one can “zoom in on” the image about 2x and 5.5x while maintaining the same clarity (or pixilation – distance between adjacent pixels) as the D1 and CIF recorded images respectfully.
This difference (HD vs. D1 or CIF) is HUGE (and even greater when considering the higher resolution range of MP-IP cameras) as this level of image resolution is often the difference between identifying a subject or capturing a license plate who’s face/numbers are legible vs. one that is merely a blur.
To see some real world pictorial examples of HD camera image quality please click here.
75 (horizontal) pixels when recorded at CIF,
150 (horizontal) pixels (~2x CIF) when recorded at D1, and,
385 (horizontal) pixels (~5x CIF) when recorded at HD.
When considering the post recorded zoom capability of the HD image, one can “zoom in on” the image about 2x and 5.5x while maintaining the same clarity (or pixilation – distance between adjacent pixels) as the D1 and CIF recorded images respectfully.
This difference (HD vs. D1 or CIF) is HUGE (and even greater when considering the higher resolution range of MP-IP cameras) as this level of image resolution is often the difference between identifying a subject or capturing a license plate who’s face/numbers are legible vs. one that is merely a blur.
To see some real world pictorial examples of HD camera image quality please click here.